
PROGRAMA
12 de marzo de 2021 – en línia
XERRADES FLAIX
Fes clic en el + per més informacions

Javier Argüello Luengo
En Javier Argüello Luengo va graduar-se en Física i Matemàtiques a la Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) per seguir desprès amb els seus estudis de post-grau al Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics (Garching, Alemanya) i al Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics (Waterloo, Canadà). Actualment és un PhD fellow de “La Caixa” i part del grup de Teoria de nanofotònica Quàntica de l’ICFO, dirigit pel Prof. Darrick Chang. La seva recerca es centra en crear propostes experiments que generin interaccions fortes entre la llum i la matèria, i la seva aplicació en l’àmbit de les simulacions quàntiques analògiques.Col·labora amb l’equip de outreach de l’ICFO i l’associació d’estudiants QuinteScience.

LisA Saemisch
La Lisa Saemisch va començar a estudiar física a Alemanya fa més de 10 anys i es va mudar a Barcelona al 2014 per fer una estada a l’ICFO, on va desenvolupar un sistema d’imatge per a un experiment xulíssim sobre gasos quàntics. La fantàstica comunitat de l’ICFO, les moltes hores de sol i la cultura local van fer que ella es quedés a l’ICFO al grup de nanofotònica molecular.
Ara està investigant la interacció entre moltes molècules individuals amb diferent antenes molt petites i defendrà la seva tesi en menys de dos mesos per obtenir el seu doctorat.

Guillermo Gerling
En Guillermo Gerling va estudiar enginyeria química i, desprès de treballar durant alguns anys a l’indústria, va decidir especialitzar-se en energies renovables i fer un doctorat en energia solar fotovoltaica. Des del 2018 treballa com a investigador a l’ICFO, desenvolupant cel·les solars transparents per a la seva aplicació a finestres i façanes d’edificis.

Claudia Valdés
La Claudia P. Valdés va estudiar física a Colòmbia on va continuar amb un màster en l’àrea d’òptica. Entre el 2011 i el 2014, va realitzar el seu doctorat a l’ICFO en el grup d’òptica mèdica, desenvolupant una tècnica per obtenir imatges amb làser del flux sanguini. Va tornar a Colòmbia on va alternar el seu treball com a especialista en imatges de microscòpia en una empresa i un projecte d’investigació en òptica mèdica. El 2019, va tornar a l’ICFO com a investigadora del grup de microscòpia òptica de super-resolució i nanoscopia, per treballar en el desenvolupament d’un instrument per obtenir imatges en alta resolució de la retina.
PROJECTES
Fes clic en el + per més informacions (tots els resums són en anglès)

Josep Amigó - En la recerca de la llum
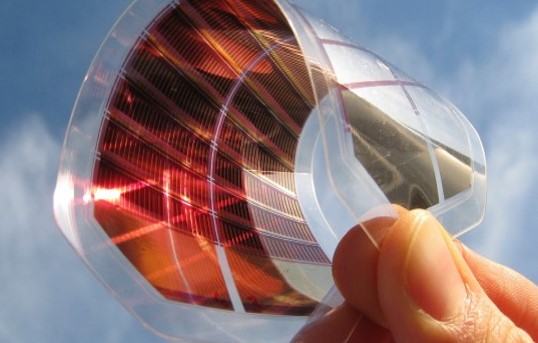
Gina Arnau Torner - The future possibilities of solar cells
Escola Frederic Mistral – Tècnic Eulàlia – Barcelona (2 Bat)

Júlia Yong Bausà Dewald - Estudi de la llum. Una aproximació de la Teoria Ondulatòria
Maria Jie Bolós Gago - Escoltant els colors
Escola Virolai – Barcelona (2 Bat)
Tutor: José Luis Touron
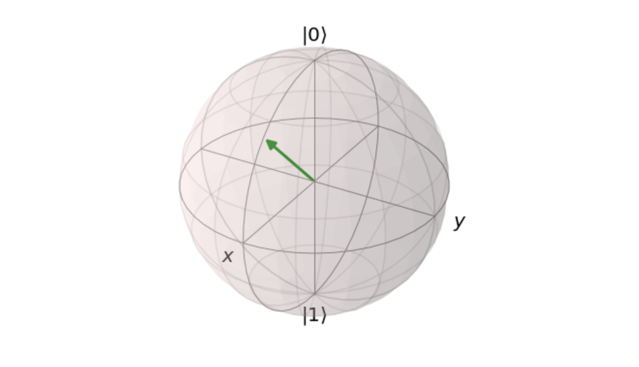
Carla Caro Villanova - Quantum annealing: an insight into its current potential
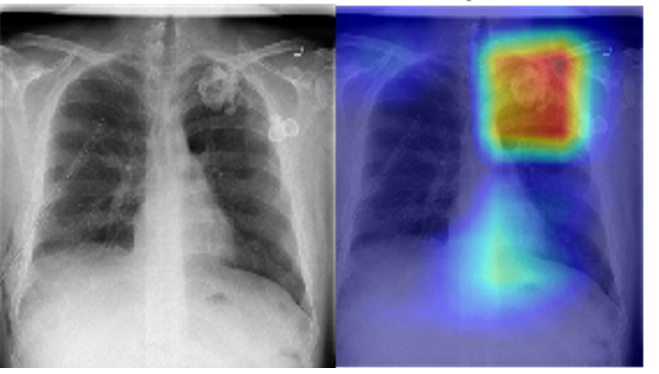
Marta Díez Asensio - Creació d’una xarxa neuronal artificial per a la detecció de quatre malalties pulmonars
In November, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), on the occasion of the celebration of the International Day of Radiology published the following headline:
“Two-thirds of the world’s population does not have access to diagnostic imaging” and continued “Between 70% and 80% of diagnostic problems can be solved through the basic use of X-ray and/or ultrasound examinations”.
“Two-thirds of the world’s population does not have access to diagnostic imaging” and continued “Between 70% and 80% of diagnostic problems can be solved through the basic use of X-ray and/or ultrasound examinations”.
Given the important statistics supported by the headline, I proceeded to read the article. Firstly, the technical details of the statistics studied were presented, which showed that the most affected countries were South America, South Africa and some Asian countries. And then, at the bottom of the publication, a study carried out by Swiss researchers was mentioned. These researchers presented a medical radiology device adapted to the economic and environmental conditions of the affected countries. These devices would facilitate the implementation of medical resources in underdeveloped countries.
In this research, a deep convolutional neural network is constructed for the diagnosis of four lung diseases (edema, tumor, cardiomegaly and pneumothorax). The model is designed to analyze X-ray images produced by the radiological medical device mentioned before. To do this I study the physical characteristics of these devices and add to the AI model the specifications needed which will be responsible for producing a medical diagnosis by analyzing these images.
To make the model I use the Chest X-ray 8 database. This dataset contains about 100,000 X-ray images of 32,000 different patients. For the verification of the results the results produced by the deep convolutional neural network, the diagnosis made by three expert radiologists are compared with the modelo. In addition, by means of ROC curve measurements, the area under the ROC curve and the implementation of heat maps, the program predicts a CI (confidence interval) which acts as an indicator of the veracity of the model.
The results obtained by this model are highly satisfactory. It is estimated that they are 95% correct in the diagnosis of the four diseases studied.

Ariadna García Zaera - Build your own Michelson Interferometer
Albert Jiménez Isábal - Quantum cryptography at the service of the citizens
-
Bias in the selection of bases
-
Initial number of qubits

Marc López Alonso - Evidències experimentals de la relativitat

Oriol Morros Vilaseca i Alejandro Nuñez Navarro - BK-SHOOTS

Marçal Muñoz Salat - Criptografia

Leonel Fernando Nabaza Ruibal - El potencial del grafè per a la dessalinització de l’aigua de mar
Daniel Rodríguez Ruiz - La física te puede curar
Marc Silvestre i Claros - Computació quàntica
Aquesta activitat és cofinançada pel Fons Europeu de Desenvolupament Regional (FEDER) de la Unió europea, en el marc del Programa operatiu FEDER de Catalunya 2014-2020, amb el suport de la Secretaria d’Universitats i Recerca del Departament d’Empresa i Coneixement de la Generalitat de Catalunya pels clústers de tecnologies emergents amb l’objectiu de valorització i transferència de resultats (Projectes GraphCAT 001-P-001702 i QuantumCAT 001-P-001644).


